

Cloud offers benefits, but poses challenges at the same time. One such challenge is in coping with numerous cloud services coupled with an ever-widening array of devices. A solution for enterprises is to adopt a distributed architecture in the form of a next-gen cloud data center. This maximizes performance, while achieving agility and simplicity of management.
A distributed data center set-up comprises edge, core and extended clouds, with workloads allocated to each, depending on individual nature.
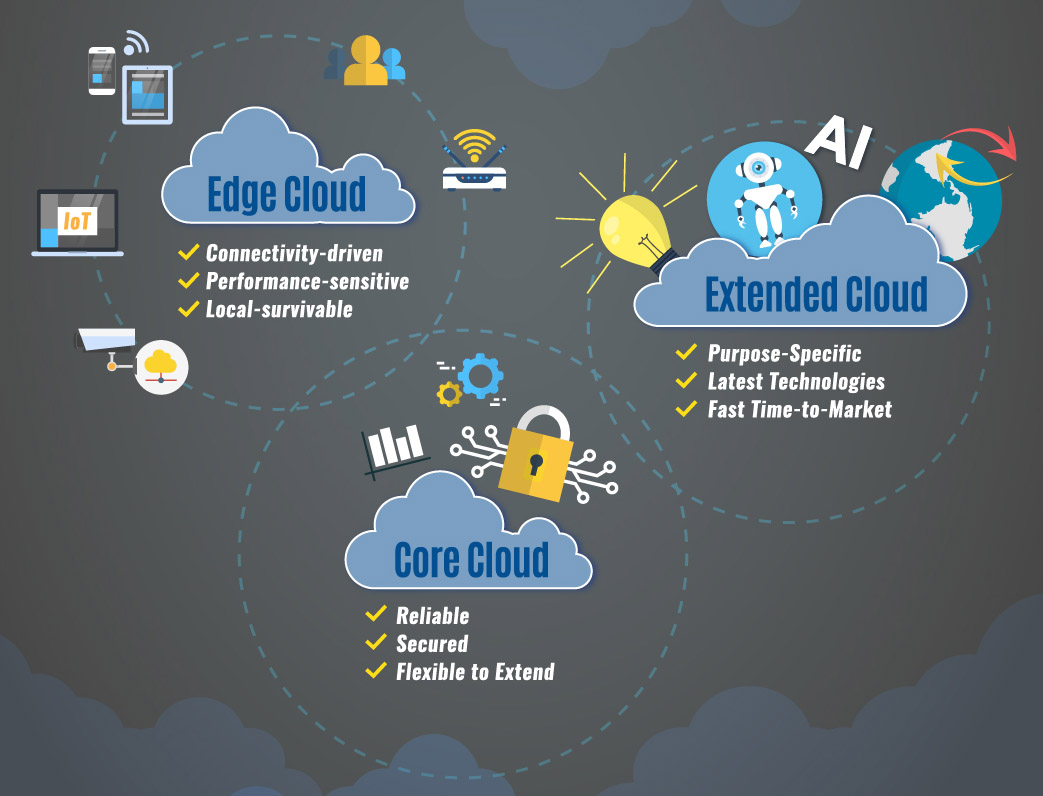
Edge Cloud – brings processing close to end-points for time-sensitive applications, so workloads do not need to be sent to a remote cloud or centralized system for processing. Eliminating the distance and time it takes to send data to a centralized source means processing and analysis can be done in real time, without bottleneck worries caused by bandwidth restrictions. Another benefit is in boosting the efficiency of applications, thanks to lower latency. An edge cloud solution should therefore be connectivity-driven, performance-sensitive and based on local survivable infrastructure.
Core Cloud – is ideal for heavy processing and storage to support business critical applications and host sensitive data. It is crucially important to enforce enterprise security policies with resilience to ensure data protection. Of equal importance is the ability to extend the network to connect with multiple edge and extended clouds. A core cloud should therefore be a secure platform with highly-reliable connectivity to enable extendable flexibility.
Extended Cloud – is built for purpose-specific and dynamic workloads. It can handle massive computing or sophisticated technologies such as big data analysis and machine learning. In addition, it can enable enterprises to test and develop applications without affecting business operations in a core cloud. Enterprises are also able to shorten time-to-market when deploying the latest technologies. An extended cloud should therefore be agile, scalable and able to draw on the strength of multiple public cloud services.
A distributed architecture enables enterprises to be flexible such that they can embark on test projects without any negative impact on daily operations. This enables them to remain competitive and sufficiently agile to perform well in a dynamic market environment.

Customer satisfaction is high priority among retailers and boosts the probability of repeat visits and purchases. Offering top-quality products is important, but so is creating a comfortable ...

Storing, transporting and looking after delicate products is a business fraught with challenges. We’ve talked to many customers from Food and Beverage (F&B) industry, Fast Moving Consumer Goods (FMCG) sector, and logistics industry...
Read More >>